Is There An Estate Or Inheritance Tax In Canada
There is no estate tax or inheritance tax in Canada. However, taxation may occur during the process of transferring and distributing an estate or inheritance. More specifically, income tax, capital gains, and other taxes may apply. Before a deceased persons estate is distributed, a final tax return must be filed and the bill paid. If youre the entity receiving all or part of an estate, you would not have to pay taxes on the received money or assets.
Related Reading Tax Season In Canada: What You Should Know
How Can I Avoid Paying Inheritance Tax
15 best ways to avoid inheritance tax in 2022
What Is Considered A Large Inheritance
What Is Considered a Large Inheritance? There are varying sizes of inheritances, but a general rule of thumb is $100,000 or more is considered a large inheritance. Receiving such a substantial sum of money can potentially feel intimidating, particularly if you’ve never previously had to manage that kind of money.
Also Check: What Is Self Employment Tax
What Is Estate Tax
Estate tax is the taxation of the money and assets of an individual who recently passed away. How is an estate tax administered? It depends on the persons residency, the size of their estate, and their will. Canadian estate tax laws instruct inheritances to be taxed in the hands of the deceased first through an estate tax filing. After that, the funds are distributed to the beneficiaries.
Capital Gains Tax On An Inheritance
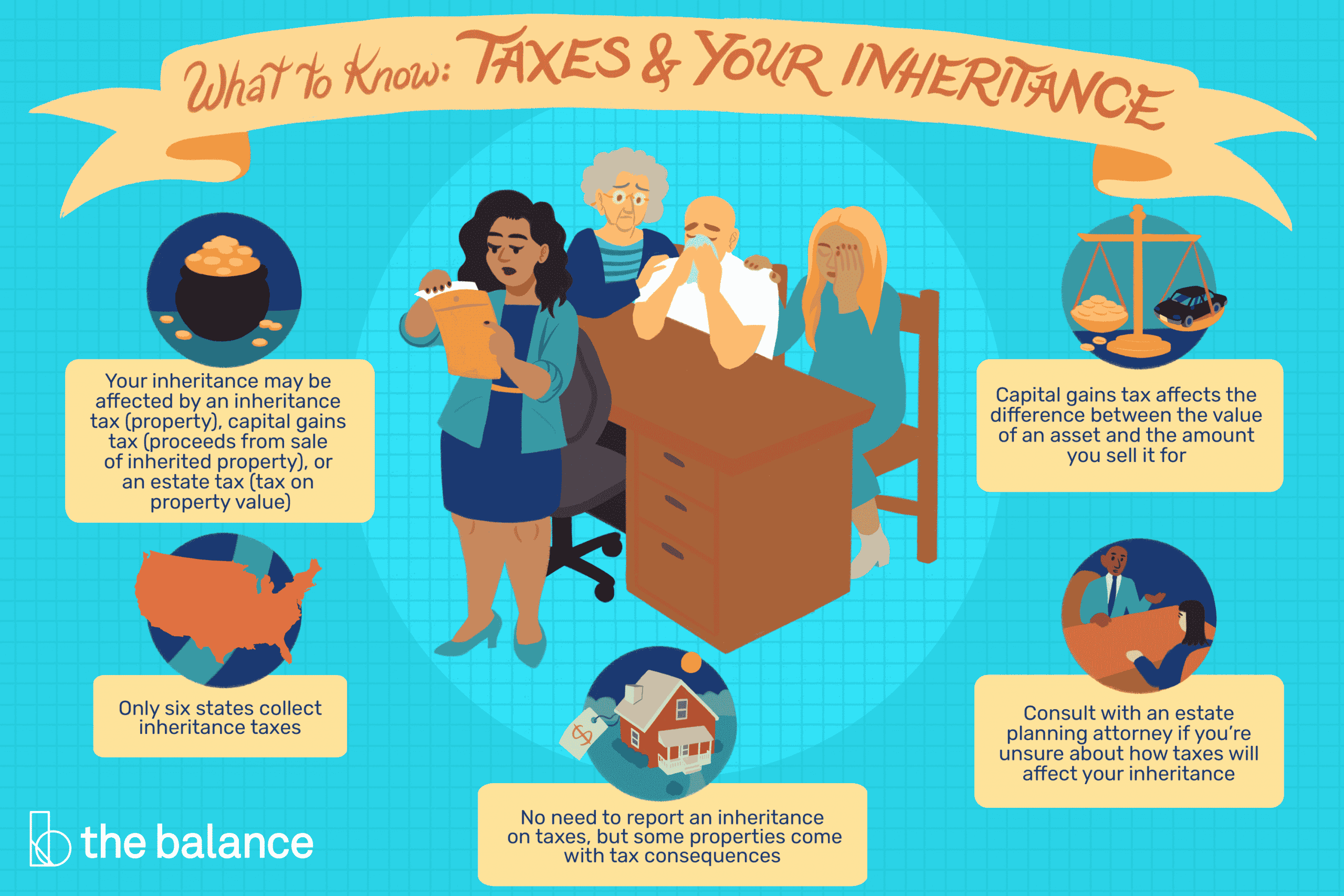
You may pay capital gains tax on assets you inherit if you sell the assets later for a profit, so its important to know their value. Capital gains tax applies whenever you sell an asset for a higher price than what you got it for. The tax applies to investments, property, and other valuables, like an art collection. There is a federal capital gains tax and every state with an income tax also collects capital gains.
In most cases, assets you inherit will have a stepped-up basis, meaning your capital gains tax would be calculated using the value of the asset when you received it instead of the value of the asset when it was first purchased. So if your parents bought a house for $100,000 decades ago and you inherit the house when its worth $300,000, then any capital gains from you selling the house are calculated as your sale price minus $300,000 . Not all assets will receive a stepped-up basis, though, so its important to understand the value of your assets for tax purposes.
Recommended Reading: Free Irs Approved Tax Preparation Courses
Put Everything Into A Trust
If you are expecting an inheritance from parents or other family members, suggest they set up a trust to deal with their assets. A trust allows you to pass assets to beneficiaries after your death without having to go through probate. Trusts are similar to wills, but trusts generally avoid state probate requirements and the associated expenses that wills typically have to go through.
- With a revocable trust, the grantor can take the assets out if necessary.
- An irrevocable trust usually ties up the assets until the grantor dies.
It may be tempting for parents to put their assets into joint names with a child, but this can actually increase the taxes the child pays.
- When joint owner dies, the other owner already owns a portion of of the assets. This means that there is a step up in cost basis on the portion that is inherited but not on the rest of the account.
- For long-held assets, this can mean a significant tax hit when the child sells the asset.
Which States Have No Inheritance Tax
States With No Income Tax Or Estate Tax The states with this powerful tax combination of no state estate tax and no income tax are: Alaska, Florida, Nevada, New Hampshire, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, and Wyoming. Washington doesn’t have an inheritance tax or state income tax, but it does have an estate tax.
Recommended Reading: Amended Tax Return Deadline 2020
What Are Inheritance Taxes
The taxes that are levied on the transfer of property from a deceased person to their heirs are known as inheritance taxes. They are based on the value of the property that is being inherited and are typically paid by the executor of the estate.
In most states, these taxes are due at the time of the deceased persons death, but some states have a delayed payment option.
| DID YOU KNOW:The most recent 2019 Survey of Consumer Finances found that the middle-class average inheritance in the US was around $110,000. |
How Much Is Uk Inheritance Tax
In the 2020/21 tax year, the standard Inheritance Tax rate is 40%, payable for most estates that are larger than £325,000. Heres an example of how it works:
Your auntie names you in her will as her sole heir. The total value of her estate is £500,000.
The first £325,000 you recieve would be tax-free. Youd pay inheritance tax at the rate of 40% on the remaining £175,000.
As a result, youd owe HMRC £70,000.
Recommended Reading: How Is Property Tax Paid
How Does The Inheritance Tax Work
Inheritance tax only applies if the deceased lived in one of the six states that levy inheritance tax. Even if you live in a state that has an inheritance tax, if the deceased lived in a state that did not have an inheritance tax you will not pay any inheritance tax.
You wont have to pay inheritance tax until after the decedents estate goes to the correct beneficiaries. Unlike estate tax, which is collected from the deceaseds assets before theyre given to beneficiaries, inheritance tax is levied after distribution. The beneficiaries are responsible for paying inheritance tax.
Each beneficiary may owe a different amount. The amount that a beneficiary owes depends on how much he or she has received, what his or her relationship to the deceased is and in which state the deceased lived.
Inheritance Tax Vs Estate Tax
Inheritance taxes and estate taxes are often lumped together. However, they are two distinct forms of taxation.
Both levies are based on the fair market value of a deceased person’s property, usually as of the date of death. But an estate tax is levied on the value of the decedent’s estate, and the estate pays it. In contrast, an inheritance tax is levied on the value of an inheritance received by the beneficiary, and it is the beneficiary who pays it.
The distinction between an estate tax and an inheritance tax with identical rates and exemptions might make no difference to a sole heir. But in some rare situations, an inheritance could be subject to both estate and inheritance taxes.
According to the Internal Revenue Service , federal estate tax returns are only required for estates with values exceeding $11.7 million in 2021 and $12.06 million in 2022. If the estate passes to the spouse of the deceased person, no estate tax is assessed.
If a person inherits an estate large enough to trigger the federal estate tax, the decedent lived or owned property in a state with an inheritance tax, and the bequest is not fully exempt under that state’s law, the beneficiary faces the federal estate tax as well as a state inheritance tax. The estate is taxed before it is distributed, and the inheritance is then taxed at the state level.
Read Also: Sales Tax And Use Texas
Do You Have To Pay Taxes On A Trust Inheritance
Estate planning is crucial to ensure the capital and assets youve spent your career amassing remain with the beneficiaries of your choosing.
When you pass, however, those assets could be subject to inheritance and estate taxes depending on where you lived and how much wealth you left to your beneficiaries.
In this article well take a look at whether beneficiaries have to pay taxes on their trust inheritances, as well as examine state and federal inheritance and estate tax rates.
Taxing A Super Death Benefit

Factors that determine how a death benefit is taxed are:
- if youre a dependant you can choose to be paid in a lump sum or as an income stream
- if youre not a dependant you can only be paid a lump sum and any taxable component will be taxed, regardless of the recipients age
- the dependents age
- if you receive the benefit as a lump sum or as an income stream lump sum payments are generally tax-free, but payments made as an income stream may be subject to tax
- if the super is tax-free or taxable
Also Check: Local County Tax Assessor Collector Office
Tax On Superannuation Death Benefits
When a person dies and they have superannuation, their super will be paid out to their nominated beneficiary. This is called a super death benefit. Depending on who receives the benefit determines how taxes will be applied.
The ATO advises:
Different rules exist for who is a dependent when making a super death benefit payment and the resulting tax treatment .
Super law sets out who a death benefit is payable to and taxation law sets out how the benefits will be taxed.
The ATO website has more information regarding who is considered a dependant under superannuation law and who is a dependant under taxation law.
If you want to leave your super to someone other than a dependant, you can contact your super provider to set up a binding death benefit nomination.
Rrsps And Other Pensions
When you leave untaxed accumulations in your RRSP or RRIF, you are deemed to have received the FMV of all assets in your RRSP or RRIF immediately prior to death.
If there is a surviving spouse, the assets may be transferred tax-free to that persons registered plan .
If there is no surviving spouse, the RRSP assets are transferred to the estate . Any decrease in value of RRSP assets while held in the estate may be used to decrease the income reported on the deceaseds final return.
Read Also: Corporate Tax Rate In India
Federal State And Inheritance Tax Rules Explained
When a person dies, their assets could be subject to estate taxes and inheritance taxes, depending on where they lived and how much they were worth. While the threat of estate taxes and inheritance taxes does exist, in reality, the vast majority of estates are too small to be charged a federal estate tax, which, as of 2021, applies only if the assets of the deceased person are worth $11.70 million or more. That exemption increases to $12.06 million in 2022.
What’s more, most states have neither an estate tax, which is levied on the actual estate, nor an inheritance tax, which is assessed against those who receive an inheritance from an estate.
Indeed, the number of jurisdictions with such levies is dropping, as political opposition has risen to what some criticize as death taxes. That said, a dozen states plus the District of Columbia continue to tax estates, and a half dozen levy inheritance taxes. Maryland collects both.
As with federal estate tax, these state taxes are collected only above certain thresholds. And even at or above those levels, your relationship to the decedentthe person who diedmay spare you from some or all inheritance tax. Notably, surviving spouses and descendants of the deceased rarely, if ever, pay this levy.
Inheriting Property From A Non
Bruce lives in Sacramento. His Aunt Victoria lived in another state and recently passed away, leaving Bruce with an inheritance. Victorias estate is subject to federal tax laws and the tax laws of the state she lived in.
If Victoria lived in a state like Iowa, Kentucky, or Pennsylvania that has an inheritance tax, Bruce would have to pay the tax on the property she leaves him. This includes the fair market value of any real property, such as a home or farm, and any monetary assets, including bank accounts, that are based in that state.
Recommended Reading: Sale Of Second Home Tax Treatment
How Do Canadian Inheritance Tax Laws Work If The Estate Is Not Inherited By A Surviving Spouse Or Common
The deceased is considered to have sold all of his or her capital property for Fair Market Value immediately prior to death. This includes, with certain exceptions, all the deceased persons non-registered assets .
If any of these assets have gone up in value since their acquisition, the estate will owe taxes on the capital gain in the year of death. A capital gain is the difference between the fair market value of the item when purchased and the fair market value of the same item at the date of death.
For any registered assets , the deceased person is deemed to have received the fair market value of his or her plan assets immediately prior to death. This amount must be included in the income of the deceased persons tax return.
Does Inheritance Affect Social Security
Social Security is not a means-tested program, which means that your eligibility for Social Security is not affected by any receipt of assets or income that you receive from an inheritance. Therefore, if you are receiving Social Security, receipt of inheritance will not have an effect on your Social Security payments.
Read Also: Where Is My California Tax Refund
Do Beneficiaries Pay Taxes On Inherited Money
Asked by: Bailey Kemmer
Beneficiaries generally don’t have to pay income tax on money or other property they inherit, with the common exception of money withdrawn from an inherited retirement account plan). … The good news for people who inherit money or other property is that they usually don’t have to pay income tax on it.
How Do You Get Around Inheritance Tax

How to avoid inheritance tax
Recommended Reading: How To Find 2020 Tax Return
How Do Inheritance Taxes Work
Inheritance taxes are the responsibility of beneficiaries who receive property after an individuals death. Depending on the state, these taxes can be charged on property transferred via a will, a trust or a deed. They can also be charged on property that transfers via intestate laws of succession, which determine who inherits if the deceased hasnt provided instructions.
The major difference between inheritance and estate tax is who pays the tax, Park says. Estate taxes are paid out of the estate, off the top, before any money is distributed to heirs. Inheritance tax is paid by the beneficiary once the money has been received.
Each state sets its own rules for how inheritance taxes work. Additionally, some counties may have their own inheritance tax. The tax is generally a percentage of the value of all the property inherited, including money, real estate and personal property. The specific percentage may depend upon the relationship of the heir to the deceased person.
The IRS generally doesnt consider inheritances to be taxable income, so you likely wont have to pay federal income tax on any inheritance you receive. But if you inherit property that generates income , youll likely have to pay tax on that income.
How Much Money Can You Have Before Probate
The short answer is that you can inherit a significant sum of money without paying state or federal income taxes. The federal government does not have an inheritance tax, but half a dozen states do:
Even these states vary when it comes to the implementation of the inheritance tax. The amount of taxes the estate pays before the inheritors receive their money may also rise and fall based on the estates worth.
Don’t Miss: Penalty For Filing Taxes Late If I Owe Nothing
What Is The Difference Between An Inheritance Tax And An Estate Tax
Inheritance tax and estate tax are two different things. Estate tax is the amount that’s taken out of someone’s estate upon their death, while inheritance tax is what the beneficiary â the person who inherited the wealth â must pay when they receive it. One, both, or neither could be a factor when someone dies.
How Can I Avoid Estate Taxes
Keeping your estate under the threshold is one way to avoid paying taxes. Other methods include setting up trusts, such as an intentionally defective grantor trust, which separates income tax from estate tax treatment, transferring your life insurance policy, so it won’t be counted as part of your estate, and making strategic use of gifting.
Recommended Reading: Property Taxes In Austin Texas
Potential Tax Concerns For Inheritances
As mentioned, the estate tax is only an issue for people dying with over $12.06 million . The individual heirs are generally not responsible for the taxes as the duty to collect and pay the estate tax is the responsibility of the executor or successor Trustee. As of 2022, states that impose inheritance tax include Minnesota, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Nebraska, Maryland, and Iowa. Here is a link to those states that have an estate tax over and above the Federal estate tax.
Some other situations in which Florida beneficiaries may have to pay some form of taxes on inheritances include: