Medicare Surtax On Capital Gains Income
There may be additional taxes on investment income or lost tax deductions for people with higher incomes. For example, married taxpayers with incomes of more than $250,000 will also be required to pay an additional 3.8% net-investment surtax. This Medicare surtax is applied to all investment income regardless of whether the capital gains are long-term or short-term capital gains. This threshold is not pegged to inflation, so each year, more taxpayers can expect to get hit with the Net Investment Income Tax .
Idaho To Consider Flat Income Tax In Special Session
Inflation is when the general price of goods and services increases across the economy, reducing the purchasing power of a currency and the value of certain assets. The same paycheck covers less goods, services, and bills. It is sometimes referred to as a hidden tax, as it leaves taxpayers less well-off due to higher costs and bracket creep, while increasing the governments spending power.
A tax bracket is the range of incomes taxed at given rates, which typically differ depending on filing status. In a progressive individual or corporate income tax system, rates rise as income increases. There are seven federal individual income tax brackets the federal corporate income tax system is flat.
The standard deduction reduces a taxpayers taxable income by a set amount determined by the government. It was nearly doubled for all classes of filers by the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act as an incentive for taxpayers not to itemize deductions when filing their federal income taxes.
An individual income tax is levied on the wages, salaries, investments, or other forms of income an individual or household earns. The U.S. imposes a progressive income tax where rates increase with income. The Federal Income Tax was established in 1913 with the ratification of the 16th Amendment. Though barely 100 years old, individual income taxes are the largest source of tax revenue in the U.S.
Earned Vs Unearned Income
Why the difference between the regular income tax and the tax on long-term capital gains at the federal level? It comes down to the difference between earned and unearned income. In the eyes of the IRS, these two forms of income are different and deserve different tax treatment.
Earned income is what you make from your job. Whether you own your own business or work part-time at the coffee shop down the street, the money you make is earned income.
Unearned income comes from interest, dividends and capital gains. It’s money that you make from other money. Even if you’re actively day trading on your laptop, the income you make from your investments is considered passive. So in this case, “unearned” doesn’t mean you don’t deserve that money. It simply denotes that you earned it in a different way than through a typical salary.
The question of how to tax unearned income has become a political issue. Some say it should be taxed at a rate higher than the earned income tax rate, because it is money that people make without working, not from the sweat of their brow. Others think the rate should be even lower than it is, so as to encourage the investment that helps drive the economy.
Recommended Reading: How To Report Coinbase On Taxes
How To Avoid Capital Gains Tax On A Rental Property
Just like selling a primary residence, you can subtract the cost of improvements, real estate commissions and closing costs from the gain you earned on your rental property. Thatll lower your tax burden some, but the really cool way to avoid capital gains taxes is doing a 1031 exchange. Ugh, the IRS and their numbered forms. But hang with us. Thisll be worth it.
A 1031 like-kind exchange allows you to defer paying capital gains taxes if you reinvest the proceeds from the sale of a property into another similar property. Thats right: If you sell a rental home and buy another with the money you made on that sale, you wont have to pay capital gains taxes on the sale. The IRS allows you to do as many 1031 exchanges as you want, but as soon as you stop investing your proceeds into similar properties, youll have to pay capital gains taxes.
The IRS is somewhat flexible on the term similar. For instance, you could sell a rental home and buy a commercial property or an apartment complex and defer capital gains taxes. But you couldnt sell a home and invest the money in mutual funds or some other investment like cryptocurrency . Well, you could. Youll just have to pay taxes on it.
We said it before, but its worth repeating: Plan ahead when selling a rental property.
Topic No 409 Capital Gains And Losses
Almost everything you own and use for personal or investment purposes is a capital asset. Examples include a home, personal-use items like household furnishings, and stocks or bonds held as investments. When you sell a capital asset, the difference between the adjusted basis in the asset and the amount you realized from the sale is a capital gain or a capital loss. Generally, an asset’s basis is its cost to the owner, but if you received the asset as a gift or inheritance, refer to Topic No. 703 for information about your basis. For information on calculating adjusted basis, refer to Publication 551, Basis of Assets. You have a capital gain if you sell the asset for more than your adjusted basis. You have a capital loss if you sell the asset for less than your adjusted basis. Losses from the sale of personal-use property, such as your home or car, aren’t tax deductible.
Recommended Reading: How To Calculate The Sales Tax
What’s The Difference Between A Short
Generally, capital gains and losses are handled according to how long you’ve held a particular asset known as the holding period. Profits you make from selling assets youve held for a year or less are called short-term capital gains. Alternatively, gains from assets youve held for longer than a year are known as long-term capital gains. Typically, there are specific rules and different tax rates applied to short-term and long-term capital gains. In general, you will pay less in taxes on long-term capital gains than you will on short-term capital gains. Likewise, capital losses are also typically categorized as short term or long term using the same criteria.
How To Report And Pay The Tax
Only individuals owing capital gains tax are required to file a capital gains tax return, along with a copy of their federal tax return for the same taxable year. The capital gains tax return is due at the same time as the individual’s federal income tax return is due. Individuals who receive a filing extension for their federal income tax return are entitled to the same filing extension for their capital gains tax return. However, a filing extension does not extend the due date for paying the capital gains tax due.
Penalties will apply to late returns. Additional penalties and interest will apply to late payments.
Don’t Miss: Travis County Tax Office – Main
Capital Gains Taxes On Collectibles
If you realize long-term capital gains from the sale of collectibles, such as precious metals, coins or art, they are taxed at a maximum rate of 28%. Remember, short-term capital gains from collectible assets are still taxed as ordinary income. The IRS classifies collectible assets as:
- Works of art, rugs and antiques
- Musical instruments and historical objects
- Stamps and coins
- Alcoholic beverages
- Any metal or gem
The latter point is worth reiterating: The IRS considers precious metals to be collectibles. That means long-term capital gains from the sale of shares in any pass-through investing vehicle that invests in precious metals are generally taxed at the 28% rate.
Capital Gains Tax Definitions And Rates
Capital assets generally include everything owned and used for personal purposes, pleasure, or investment, including stocks, bonds, homes, cars, jewelry, and art. The purchase price of a capital asset is typically referred to as the assets basis. When the asset is sold at a price higher than its basis, it results in a capital gain when the asset is sold for less than its basis, it results in a capital loss. Although capital gains taxes typically apply to the returns from any capital asset, including housing, U.S. homeowners benefit from a generous exemption for gains resulting from the sale of their primary residence, set at $250,000 for single filers .
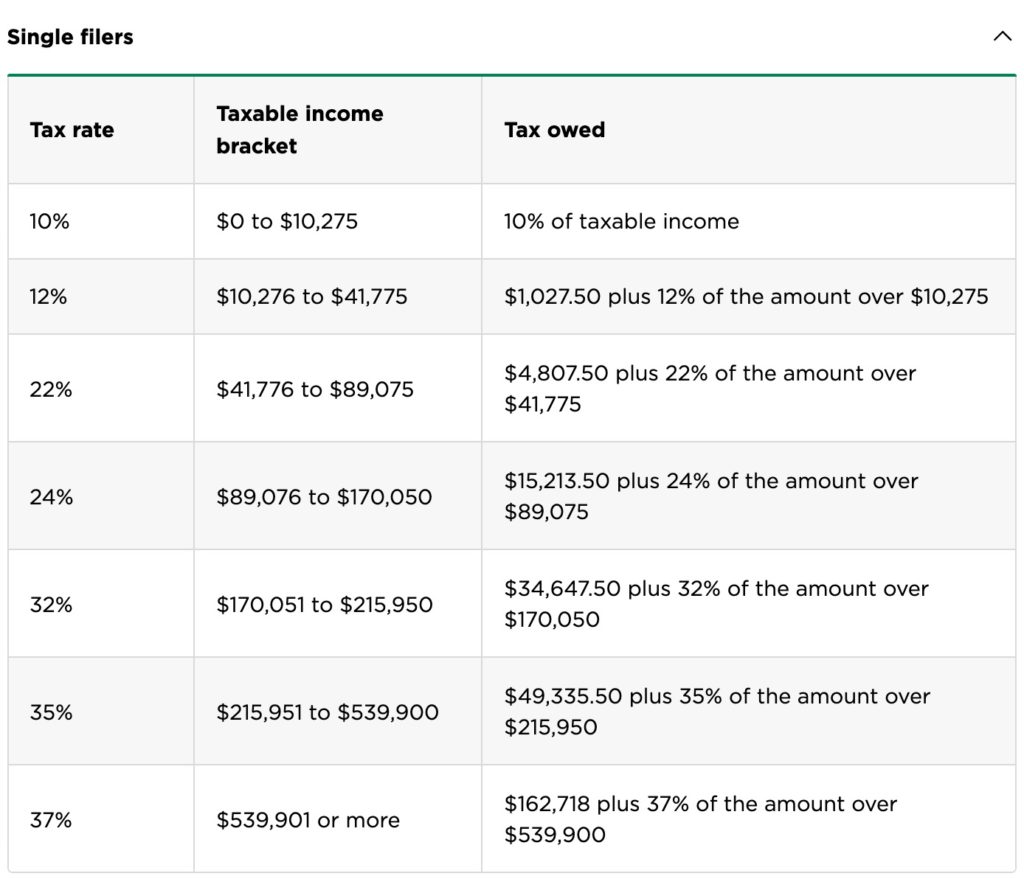
In the United States, when a person realizes a capital gain, they face a tax on that gain. Capital gains tax rates vary depending on two factors: how long the asset was held and the amount of income the taxpayer earns. If an asset was held for less than one year and then sold for a profit, it is classified as a short-term capital gain and taxed as ordinary income. If an asset was held for more than one year and then sold for a profit, it is classified as a long-term capital gain. Table 1 indicates the tax rates applicable to long-term capital gains for tax year 2019.
| MAGI above $200,000 |
Read Also: New Jersey Tax Refund Status
How To Calculate Your Tax Bill
To calculate your capital gains tax bill, youll need a few pieces of information.
First, you need to know how much taxable income you have in a year. To calculate this, simply add all of the money youve earned and subtract deductions such as retirement account contributions and the standard deduction.
Then, you need to calculate your short-term capital gains. To do this, youll need to know the price you paid for every investment you sold during the year plus the price at which you sold those investments. If that sounds like a lot, the good news is that your brokerage should send you this information.
Subtract your short-term losses from your short-term gains to find your net short-term gains for the year. Multiply those gains by the tax rate for the tax bracket you fall into to find your short-term capital gains tax for the year.
Note: You might wind up moving to a higher tax bracket due to your capital gains, in which case a portion of the gains get taxed at the higher rate, which can make the math slightly more complicated. The higher rate will only apply to income above the threshold for that tax bracket.Learn more about how taxes work
If your losses exceed the gains, you can deduct up to $3,000 of those losses from your normal income to reduce your tax bill. If you lost more than $3,000, you may carry those losses to future years to take deductions in the future.
A Guide To The Capital Gains Tax Rate: Short
OVERVIEW
This guide can help you better understand the different rules that apply to various types of capital gains, which are typically profits made from taxpayers sale of assets and investments.
|
Key Takeaways Profits you make from selling most assets are known as capital gains, and they are generally taxed at different rates depending on how long you have held the asset. Gains you make from selling assets youve held for a year or less are called short-term capital gains, and they generally are taxed at the same rate as your ordinary income, anywhere from 10% to 37%. Gains from the sale of assets youve held for longer than a year are known as long-term capital gains, and they are typically taxed at lower rates than short-term gains and ordinary income, from 0% to 20%, depending on your taxable income. If your investments end up losing money rather than generating gains, you can typically use those losses to reduce your taxes. |
The U.S. Government taxes different kinds of income at different rates. Some types of capital gains, such as profits from the sale of a stock that you have held for a long time, are generally taxed at a more favorable rate than your salary or interest income. However, not all capital gains are treated equally. The tax rate can vary dramatically between short-term and long-term gains. Understanding the capital gains tax rate is an important step for most investors.
Don’t Miss: Selling House Capital Gain Tax
Capital Gains Go Overwhelmingly To Wealthy White Households
Capital gains are generated by wealth. Because wealth is highly concentrated, so is capital gains income. About 85 percent of capital gains go to the wealthiest 5 percent of taxpayers 75 percent go to the top 1 percent of taxpayers. Wealthy households are disproportionately white: white families are three times likelier than families of color to be in the top 1 percent.
The Impact Of A Capital Gains Tax

Capital gains taxes affect more than just shareholders there are repercussions across the entire economy. When multiple layers of tax apply to the same dollar, reducing the after-tax return to saving, taxpayers are incentivized to consume immediately rather than save. Take the following example from our primer on capital gains taxes:
Suppose a person makes $1,000 and pays individual income taxes on that income. The person now faces a choice: should I save my after-tax money or should I spend it? Spending it today on a good or service would likely result in paying some state or local sales tax. However, saving it would mean paying an additional layer of tax, such as the capital gains tax, plus the sales tax when the money is eventually used to purchase a good or service. This second layer of tax reduces the potential return that a saver can earn on their savings, thus skewing the decision toward immediate consumption rather than saving. By immediately spending the money, the second layer of tax can be avoided.
Read Also: Irs.gov File Taxes For Free
Qualified Small Business Stock
The tax treatment of a qualified small business stock depends on when the stock was acquired, by whom, and how long it was held. To qualify for this exemption, the stock must have been acquired from a QSB after Aug. 10, 1993, and the investor must be a noncorporate entity that held the stock for at least five years.
A QSB is generally defined as a domestic C corporation with aggregate gross assets that have never exceeded $50 million at any point since Aug. 10, 1993. Aggregate gross assets include the amount of cash held by the company, as well as the adjusted bases of all other property owned by the corporation. Additionally, the QSB must file all required reports.
Only certain types of companies fall under the category of a QSB. Firms in the technology, retail, wholesale, and manufacturing sectors are eligible as QSBs, while those in the hospitality industry, personal services, financial sector, farming, and mining are not.
This exemption originally allowed the taxpayer to exclude 50% of any gain from the sale of QSB stock. However, it was later increased to 75% for QSB stock acquired from Feb. 18, 2009, to Sept. 27, 2010, and then to 100% for QSB stock acquired after Sept. 27, 2010. The gain that is eligible for this treatment has a cap of $10 million, or 10 times the adjusted basis of the stockwhichever is greater.
Jeffrey H Kahn Harry M Walborsky Professor & Associate Dean For Business Law Programs Florida State University College Of Law
If Washington puts state capital gains taxes in place, might that pave the way for other states to do the same?
I do not think that the addition of a capital gains tax in the state of Washington would have much of a bearing on whether other states decide to impose one. The other considerations on whether to impose a state-level capital gains tax are likely more important.
For example, a capital gains tax on top of a higher federal tax might lead some to flee the state or at least make it less desirable to move there. We have seen a general trend of people moving from high tax states to low tax states and state governments are certainly aware of this.
I believe the pandemic has sped up the remote worker movement which allows people to be even more mobile and so tax rates may play an even larger role in residency decisions.
If the government expresses interest in raising capital gains taxes, could we see a stock sell-off in response? How might that affect the greater economy?
I believe a sell-off is certainty, especially if the increase is paired with the repeal of section 1014 which provides for a step-up basis at death.
The loss of value in the market will impact pension and retirement funds and make investments less attractive. It is unclear whether an increase will actually raise significantly more revenue so the trade-off does not appear to be worth it.
Recommended Reading: Is Auto Insurance Tax Deductible
Capital Gain Tax Rates
The tax rate on most net capital gain is no higher than 15% for most individuals. Some or all net capital gain may be taxed at 0% if your taxable income is less than or equal to $40,400 for single or $80,800 for married filing jointly or qualifying widow.
A capital gain rate of 15% applies if your taxable income is more than $40,400 but less than or equal to $445,850 for single more than $80,800 but less than or equal to $501,600 for married filing jointly or qualifying widow more than $54,100 but less than or equal to $473,750 for head of household or more than $40,400 but less than or equal to $250,800 for married filing separately.
However, a net capital gain tax rate of 20% applies to the extent that your taxable income exceeds the thresholds set for the 15% capital gain rate.
There are a few other exceptions where capital gains may be taxed at rates greater than 20%:
Note: Net short-term capital gains are subject to taxation as ordinary income at graduated tax rates.