Apportionment Required If Expenses Benefit Entire House
The deductibility of an expense depends upon whether it benefits just the home office, your entire house including your home office or portions of the house that do not include your home office.
Expenses that exclusively benefit your business are considered “direct” home office expenses.
Direct expenses are fully deductible. Expenses that benefit the entire home are considered “indirect” home office expenses that are proportionately deductible based upon the percentage of business use of the home.
Expenses that benefit only the personal portion of the home are not deductible at all.
Home Improvements For Medical Reasons
Specific home improvements done for medical reasons qualify for tax deductions. If your home improvement projects are designed to improve medical care for homeowners, their spouses, or other dependents, they are considered medical expenses on taxes. These projects can also be considered capital improvements if they increase property value. Home improvements that qualify as medical expenses include:
- Installing entrance and exit ramps
- Installing support bars or railings in bathrooms
- Modifying smoke detectors and fire alarms
- Installing grab bars and handrails
- Modifying staircases
Note that home improvements designed for aesthetic purposes cannot qualify for tax deductions as medical expenses. Eligible improvements should adapt the home to disabled individuals.
Rules For Home Offices
Many Canadians are or are becoming self-employed, and many choose to work out of their homes. Some businesses as well, choose to allow their employees to work remotely. Just as you needed an office as an employee when working at a business location, youll need one for your own business. The good news is the Canada Revenue Agency lets you claim your home office on your taxes however, be sure to follow the rules, otherwise, your tax claim could be denied.
Trading in your cubicle at work for a home office means possible tax deductions.
Recommended Reading: Free Irs Approved Tax Preparation Courses
How To Determine Your Home Office Deduction
You can determine the value of your deduction the easy way or the hard way.
-
With the simplified option, you arent deducting actual expenses. Instead, the square footage of your space is multiplied by a prescribed rate. The rate is $5 per square foot for up to 300 square feet of space.
-
The regular, more difficult method values your home office by measuring actual expenditures against your overall residence expenses. You can deduct mortgage interest, taxes, maintenance and repairs, insurance, utilities and other expenses.
You can use Form 8829 to figure out the expenses you can deduct.
» MORE:See our picks for this year’s best tax software
I Started Working From Home Due To The Pandemic Can I Deduct My Home Office Expenses
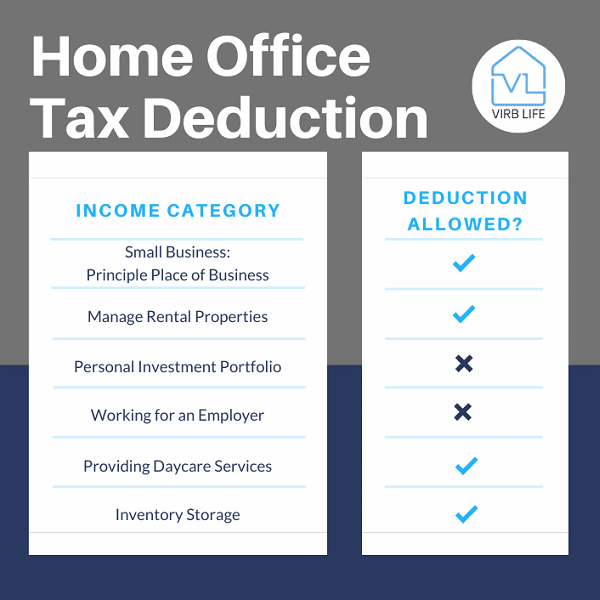
Unfortunately, the answer to that question is no. There is no tax deduction available for traditional employees to deduct the expenses related to their home office. The home office deduction youre likely familiar with is only available to self-employed people.
Many companies have provided home office stipends or financial support of some capacity for their employees throughout the pandemic while mandating they work from home. If your company has not offered to cover any of your new home office expenses, our recommendation is to reach out to your HR department or direct boss to discuss the possibility of receiving assistance. It never hurts to ask!
While working from home is convenient and comes with various perks, the increased utility cost and the need to purchase equipment to work efficiently can be a strain on your bank account. We encourage you to start a conversation with your employer about how they could help offset some of those extra costs especially if you wont be returning to the office any time soon.
Recommended Reading: California Sales Tax By Zip Code
How Much Is The Self
The self-employment tax is 15.3%. The self-employed pay 12.4% for Social Security and 2.9% for Medicare. Remember that your self-employment tax is a deductible expense. The Internal Revenue Service will allow you to count half of the self-employment tax amount, the amount that your employer usually covers, as a business deduction.
What Is The Simplified Square Footage Method
Beginning with 2013 tax returns, the IRS began offering a simplified option for claiming the deduction. This new method uses a prescribed rate multiplied by the allowable square footage used in the home.
- For 20221, the prescribed rate is $5 per square foot with a maximum of 300 square feet.
- If the office measures 150 square feet, for example, then the deduction would be $750 .
- The space must still be dedicated to business activities.
With either method, the qualification for the home office deduction is determined each year. Your eligibility may change from one year to the next.
Read Also: Are 2022 Tax Forms Available
A Place To Meet Patients Clients Or Customers
Using part of a home as a place to meet clients allows more flexibility, and it can be deducted even if there is another principal place of business. For example, if a self-employed attorney meets clients at home two days a week but works out of another office the other three days, the home office qualifies for a deduction . Use of the home to meet with patients, clients, or customers must be “substantial and integral” to the business ). Videoconferencing or occasional meetings are likely not enough.
The Home Office Deduction: Why You Probably Can’t Claim It Even If You Work From Home
You won’t qualify for this deduction if you’re a W2 employee, but you may be eligible if you freelance or own your own business.
The pandemic has shifted the way Americans work — perhaps forever. Remote work has become part of our new normal and in September of last year alone, 45% of full-time employees reported working from home in some capacity, according to a Gallup survey. And if you’re one of the millions of remote workers who works from their kitchen table daily, you may be wondering about the home office tax deduction. But, if you work for a traditional employer, you won’t qualify for this tax break.
“If someone tries to claim a home office deduction and doesn’t have an at-home business activity, be it self employment or farm activity or other business, taking the benefit without other matching tax information can create a red flag in the IRS’s system,” according to Mark Steber, chief tax information officer at Jackson Hewitt Tax Service.
Who does qualify? In short, business owners, freelancers or gig workers who use a home office or home office space 100% of the time for work reasons. But there are some caveats. Here’s everything you need to know about the home office deduction for your 2021 taxes.
Note: It’s always a good idea to consult a trusted tax advisor or tax software service to get the specifics for your particular situation.
Also Check: Lovetothe Rescue.org/tax-receipt
The Home Office Regular Method
The home office regular method requires that you calculate the percentage of your home used for business by dividing the area used for business by the total area of your home. You canât claim home office deductions greater than your gross income, but you can carry the excess deduction amount over to future years.
To use the home office regular method, you first determine what percentage of your home qualifies as home office space. Then, you multiply that percentage by the total amount of actual expenses.
To take advantage of this, youâll need good recordkeeping to keep track of each business deduction so you can claim it on your Schedule C.
How to calculate your deduction with the home office regular method
Letâs say your home is 1,200 square feet, and you use 120 square feet as office space. First, you divide to find your percentage:
120 / 1,200 = 0.10
So, you can deduct 10% of your indirect home expenses from your taxes. That includes mortgage interest, homeownerâs insurance, real estate taxes, rent, etc.
| Expense |
|---|
Business Furniture And Equipment
Most business furniture and equipment cant be written off as a deductible expense. If you buy a new desk, you cant deduct its cost.
But you can deduct the depreciation on business furniture and equipment. Items in a home office that depreciate include:
- Office furniture such as desks, files and safes
Everything except for office furniture is considered a 5-year property. Office furniture is a 7-year property. Depreciation is calculated differently for the two categories. This home office tax deduction calculator will help you calculate how much you can write off.
Don’t Miss: How To Check My Amended Tax Return
Indirect Deductions For Homeowners
As a homeowner, youâre able to claim a portion of the mortgage interest that you pay on your home against your business. If 10% of your home is used for business, then you would claim 10% of your yearly mortgage interest on Form 8829, and report the remaining 90% on Schedule A.
In addition to claiming a portion of your mortgage interest, you can also take deductions for homeownerâs insurance, repairs, real estate taxes, security, and other home-related expenses .
If you own your home outright, you can claim a depreciation deduction for the business percentage of your home. Calculating depreciation can be complex, so talking to a tax professional will ensure youâre getting the most out of this option. You can also consult Publication 587 for an IRS guide on deducting depreciation of your home.
Home Office Expenses For The Self

If youre self-employed, you can claim your home office under two conditions: 1) The work space must be your principal place of business or used exclusively for the purpose of earning income from business. 2) The space must be used on a regular and continuous basis for meeting clients, customers or patients. Its important to be realistic when claiming the size of your home office. One of the most common audit triggers is claiming inflated home office expenses.
Don’t Miss: Haven T Received Tax Return
Dues And Publications Deduction
The cost of specialized magazines, journals, and books directly related to your business is tax deductible as supplies and materials, as are dues or fees for certain professional membership organizations.
A daily newspaper, for example, would not be specific enough to be considered a business expense. On the other hand, a subscription to Nations Restaurant News would be tax deductible if you are a restaurant owner, and Nathan Myhrvolds several-hundred-dollar Modernist Cuisine boxed set would be a legitimate book purchase for a self-employed, high-end personal chef.
As for membership dues or fees, you cant deduct them for belonging to clubs organized for business, pleasure, recreation, or any other social purpose. Examples include country clubs, golf and athletic clubs, hotel clubs, sporting clubs, airline clubs, and clubs operated to provide meals under circumstances generally considered to be conducive to business discussions. However, the IRS does make exceptions for groups that it considers do not exist for entertainment purposes. These are:
- Boards of trade
- Civic or public service organizations
- Professional organizations such as bar associations and medical associations
- Real estate boards
- Trade associations
Capital Gains Exclusion Selling Your Home
Most of the tax advice out there is for buyers, but there are tax advantages for sellers too. Primarily, the capital gains you make when you sell your own home are tax free. That means that if you buy your house at one price, say $300,000, and sell it at a higher price of $450,000, your capital gains would be $150,000. Thats all tax free . This, however, only works for your primary residence and not a second home.
The limits for tax-free capital gains are $250,000 if you are single, and $500,000 for a married couple.
Recommended Reading: When Is An Estate Tax Return Required
What Are The Standard Deduction Amounts For 2022
If you have no other qualifying deductions or credits, you can take what is called the standard deduction a standardized dollar amount that reduces your taxable income based on your filing status. In 2022 the standard deductions are:
-
Single filers or married individuals filing separately: $12,950
-
Joint filers: $25,900
-
Head of household: $19,400
When it comes time to file, you can either take the standard deduction or if youre eligible for other deductions you may choose to itemize them . Bear in mind, that if you take the standard deduction, you wont be able to deduct your home mortgage interest.
Are Mortgage Points Tax Deductible
When you close on your house, typically you can also deduct any points you paid when you got the mortgage. Mortgage points are payments you make to get the loan or get it with a reduced interest rate. One point is one percent of the total home loan amount. Two points are two percent. You get the picture.
If you pay these points up front, or pay them all during the first year of ownership, you can typically deduct them. That can add up fast. If, however, you roll them into the mortgage and pay them over time, they may not add up to much in terms of a yearly deduction. Information about your points paid will be on your 1098 form from your mortgage company.
Recommended Reading: How Property Taxes Are Calculated
How Small Business Owners Can Deduct Their Home Office From Their Taxes
IRS Tax Tip 2022-10, January 19, 2022
The home office deduction allows qualified taxpayers to deduct certain home expenses when they file taxes. To claim the home office deduction on their 2021 tax return, taxpayers generally must exclusively and regularly use part of their home or a separate structure on their property as their primary place of business.
Tax Benefits Of Owning A Home
Last Updated on November 30, 2022 by Luke Feldbrugge
The tax benefits of owning a home can be a tipping point for you if you are on the edge of deciding to begin hunting for a new home. If you are a first time home buyer, some of these deductions and tax credits will surprise you. If you are a long-time homeowner, you know that a new home mortgage can help you with your tax burden for years. And if youre a seller, theres something in the tax laws for you too. Here we cover two main tax benefits of owning a home: tax credits and tax deductions.
As you are looking at the tax benefits of buying a house, its important to distinguish between tax credits and tax deductions. Both are good, but one is better. Heres the math on that
- Tax Credit is more valuable because it reduces the amount of tax you might pay, or increases your return, dollar-for-dollar. A tax credit of, say $1,000, reduces your taxes by $1,000. Thats pretty straightforward.
- Tax Deduction reduces your adjusted income, so it only reduces a percentage of the tax you will owe. A tax deduction of $1,000 reduces your taxable income by $1,000, but you probably only pay 28% of that in taxes. That means you get a reduction of $280 on your tax credits. So deductions only take away a percentage of your owed taxes.
Don’t Miss: Pto Cash Out Tax Calculator
Special Rules Govern Home Office Casualty Losses
If you qualify for the home office deduction and your home office is damaged or destroyed by a burglary or a disaster such as a hurricane, flood, fire, accident, riot, or vandalism, you may be able to deduct some of your losses as part of the home office deduction.
imply a sudden, accidental, or unusual loss. Casualty losses do not include damage from pets or progressive losses to property such as damage from erosion, termites or other insects, wood rot, and similar slow-moving causes.
If the loss occurs only to the home office, treat it as a “direct” expense that is fully deductible. If it applies to the entire home, you will need to allocate the amount between the home office portion of your house and the personal use portion. You make the allocation based upon your business use percentage. If the loss occurred only to the non-business part of the home, you may not deduct any of it as a business expense, although you may be able to deduct it as a personal expense.
Example: A severe hail and wind storm caused extensive damage to the roof of your home. The business use percentage of your home is 10 percent. Therefore, only 10 percent of the casualty loss will be deductible as a business loss. The remainder may be deductible as a personal casualty loss.
In addition, the wind caused a tree to fall through the picture window in your family room, which is not part of your home office. The amount of this loss is not prorated between the home office and the residence.
Will You Get Audited For Claiming A Home Office

No, claiming the home office deduction does not increase your audit risk. Itâs an extremely common and valid tax write-off.
This is an understandable fear for many people, and Iâm happy to put your minds at ease.
That being said, donât go nuts. Be honest about what you claim, and keep records to support it. If you try to write off more than 50% of your housing costs, that might look fishy. But if you take 20-30% and you have reliable records to back it up, donât sweat.
What are some examples of reliable records?
- Records from Zillow, your property manager, or the Recorderâs Office listing the size your home
- Bank statements or Keeper Tax records of your housing expenses
Best practice is to keep these records for three years after the date you file your return. And just to stress this again, be honest. If your home office genuinely takes up 50% of your home â claim it! Just understand that itâll be up to you to prove it was legitimate if the IRS doesnât buy it.
Sarah York, EA
Also Check: Is Mortgage Interest Tax Deductible